Sore Toe?
Let us help you
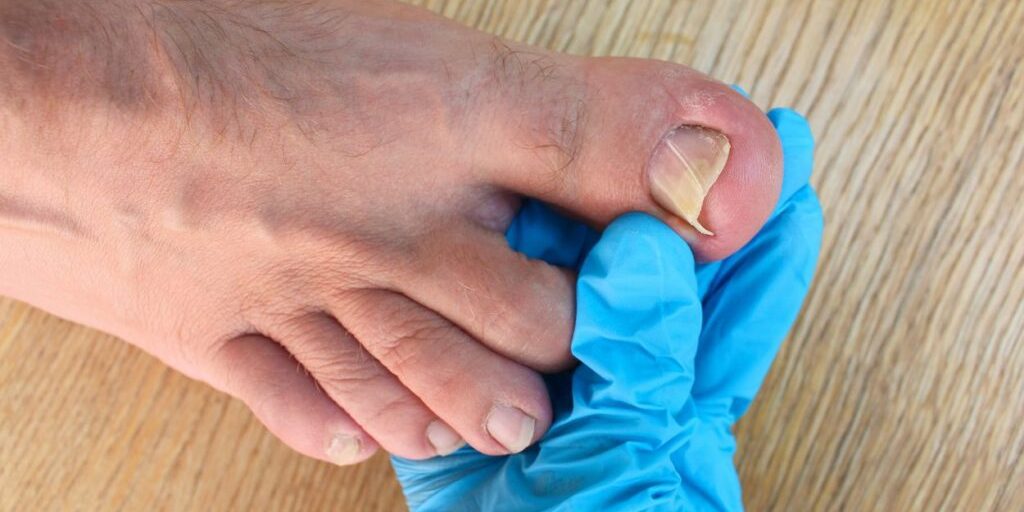
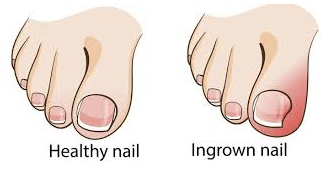
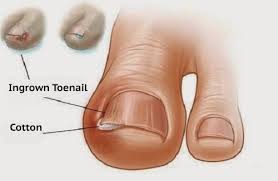
Ingrown toenails are a common condition, especially in adolescent boys and girls. It may follow injury or deformity of the nail bed. It is typically located along the lateral edges of the great toenail and represents an imbalance between the soft tissues of the nail fold and the growing nail edge. An ingrown toenail is medically referred to as onychocryptosis.
The basic cause is a redundant skin fold. It is thought to be caused / exacerbated by
- Faulty nail trimming
- Improper shoe wear (too large or small)
- Poor foot hygiene
- Injury by overly aggressive pedicures and nail picking
- Repetitive pressure or trauma to the feet or abnormal gait.
- Underlying foot and toe deformity
It is also common in some athletics, particularly stop and start sports such as tennis, soccer, and basketball.
The warm, moist environment of the feet can be a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi. These commonly include Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, dermatophytes, Candida, and Trichophyton. When there is a break in the skin from the offending nail border, these organisms can invade the area and cause an infection, swelling and granulation tissue of the nail fold.
Diagnosis
Ingrown toenail symptoms and signs include redness, pain, and swelling. Sometimes there may be a clear yellowish drainage, or if it becomes infected, pus drainage. Occasionally, ingrown toenails resolve without treatment. Painful, persistent, and recurring ingrown toenails should be treated.
Sometimes there is nail edge curving into the skin (incurvation) or a spike of nail (spicule) pressing into the skin of the nail border. When an infection is involved, there may be severe redness and swelling, drainage, pus, and a bad smell.
Treatment
- Correct comfortable footwear
- Correct nail care
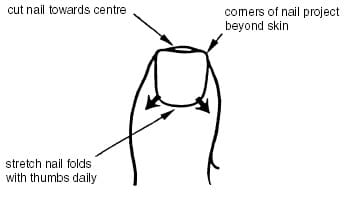
- Fashion toenails so that the corners project beyond the skin. The end of the nail (NOT the corners) should be cut squarely so that the nail can grow out of the nail fold.
- Cotton wool pledgets can be placed beneath the affected nail border to assist separation, to lift the offending edge of the nail up from the skin.
- Foot baths
- Lukewarm water foot soaks for 15-20 minutes with any one of the following options can be helpful:
- one part white vinegar to four parts water or 2 tablespoon Epsom salt per litre of water.
- Each day, after a shower or bath, use pads of both your thumbs to pull the nail folds as indicated.
- Elevate the foot and leg.
- Take oral anti-inflammatory medications, if indicated.
- If the area is infected, a course of oral antibiotics from your doctors may be needed.
Please see us at Queensland Foot Centres for personal and professional advice tailored for you.
A persisting ingrown toenail may have serious consequences. A localized infection of the nail border (paronychia) can progress to a deeper soft-tissue infection (cellulitis), which can in turn progress to a bone infection (osteomyelitis). Complications can include scarring of the surrounding skin and nail borders as well as thickened, deformed toenails (onychodystrophy).
Surgical Treatment
This is performed when the conservative treatments fail. There are many types of surgical treatments. At Top Health Doctors, we offer
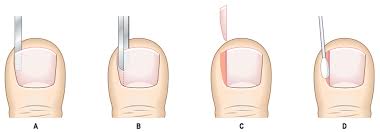
1) Wedge removal of offending nail border or corner, and phenol chemical partial matrixectomy
Or
2) Wedge resection of nail, nail bed and surgical partial matrixectomy.
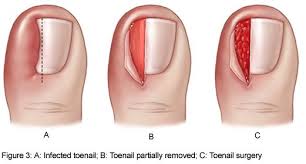
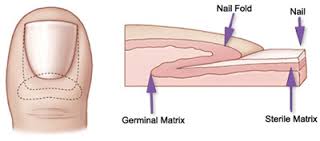
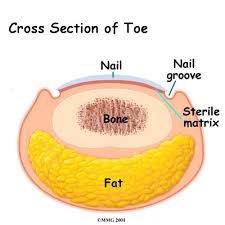
A matrixectomy is the destruction or removal of the cells where the nail grows from called the nail matrix. The nail matrix is at the base of the toenail under the skin. This procedure can be done surgically by surgical dissection or chemically (usually using Phenol) by destroying part or all of the matrix cells.